not dependent to the exact values of thresholds. So, mild
changes do not affect the results especially the validity-factors.
Comparative Results and Accuracy Assessments
After performing the proposed
SLIM
based on the selected
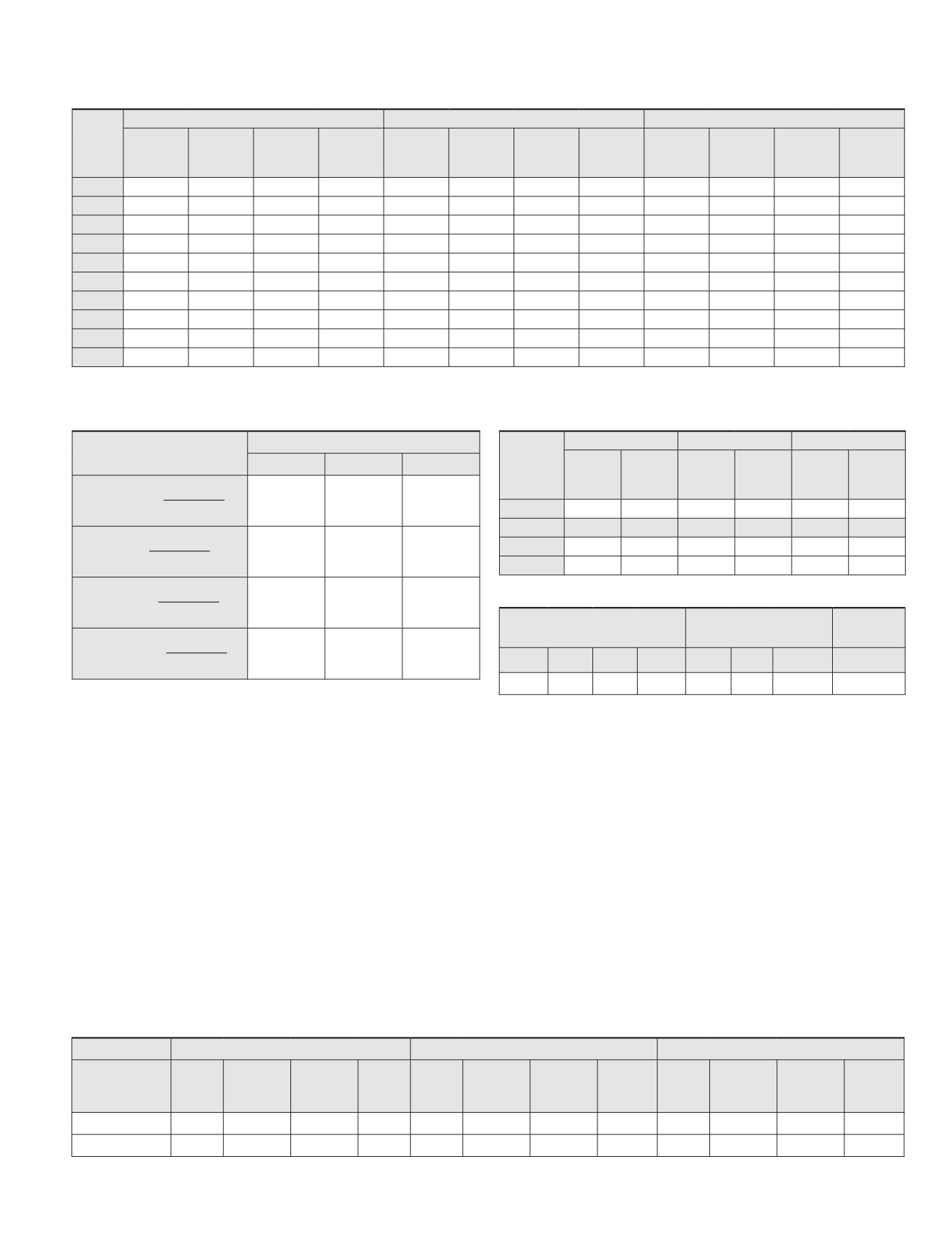
thresholds (Table 7), the obtained results for the first to third
datasets are shown both graphically (Plate 1) and quantita-
tively (Table 8). As shown in the results, all matched-lines are
found correctly (validity-factors for all datasets based on the
proposed thresholds are equal to 100 percent).
Additionally, a
RANSAC
method (Fischler and Bolles, 1981)
for linear feature-based matching was also developed and
applied on the first to third datasets to compare with the pro-
posed
SLIM
. The comparative results are shown in Table 8.
Based on the above results,
RANSAC
failed on the first
dataset for 300,000 iterations. The results of
RANSAC
show
that the validity and capacity-factors are low, which means,
the results are not reliable. Additionally, comparative results
show its higher computational time. Consequently, the results
demonstrate the superiority of the novel
SLIM
in terms of ac-
curacy as well as reliability, automation, and computational
time.
Discussion
Based on the achieved results, it can be said that the proposed
SLIM
is not dependent to the mild changes of the thresholds.
This means that selecting lower or higher values (especially
T
1
and
T
2
) will only entail changing the computational time
in most cases. As discussed earlier, the proposed
SLIM
is a
guided search (or knowledge-based) method, i.e., not a blind
or random method. On the other hand, because the
SLIM
is
a knowledge-based multilayer strategy, the reliability of the
matched-lines is 100 percent (validity-factors) in most cases.
In addition, approximately all possible inliers (capacity-
factors of more than 80 percent) could be determined using
the novel
SLIM
in a very low computational time. Hence, as
obvious from the results, the proposed
SLIM
is able to deal
T
able
4. T
he
I
nfluence
of
D
ifferent
V
alues
of
on
the
N
umber
of
M
atch
-L
ines
,
the
V
alidity
and
C
apacity
-F
actors
as well
as
C
omputational
T
ime
over
the
F
irst
to
T
hird
datasets
T
3
First Dataset
Second Dataset
Third Dataset
No. of
Match
Lines
Validity
Factor
(%)
Capacity
Factor
(%)
Comp.
Time
(m.)
No. of
Match
Lines
Validity
Factor
(%)
Capacity
Factor
(%)
Comp.
Time
(m.)
No. of
Match
Lines
Validity
Factor
(%)
Capacity
Factor
(%)
Comp.
Time
(m.)
NA
-
-
-
-
42
100
68.9
0.30
-
-
-
-
2*
NA
60
100
80
0.57
60
100
98.4
0.16
13
100
41.9
3.22
3*
NA
63
100
84
0.78
60
100
98.4
0.14
18
100
58.1
3.29
4*
NA
69
100
92
0.79
61
100
100
0.13
19
100
61.3
3.41
5*
NA
71
100
94.7
0.78
61
100
100
0.13
21
100
67.7
3.42
6*
NA
75
100
100
0.77
61
100
100
0.18
26
100
83.9
3.33
7*
NA
75
100
100
0.77
61
100
100
0.18
23
100
74.2
3.49
8*
NA
75
100
100
0.77
61
100
100
0.18
27
100
87.1
3.43
9*
NA
75
98.7
98.7
0.76
61
96.7
96.7
0.19
28
100
90.3
3.32
10*
NA
75
98.7
98.7
0.75
60
95.1
96.7
0.13
31
100
100
3.37
T
able
5. D
ifferent
R
elations
P
roposed
as
the
S
topping
-C
riterion
;
A
dditionally
, N
umber
of
I
terations
based
on
the
P
roposed
R
elations
for
E
ach
D
atasets
are
also
D
emonstrated
Proposed relations as
the stopping-criterion
No. of Iterations
1
st
Dataset 2
nd
Dataset 3
rd
Dataset
R
l
l k k
1
0 5
=
−
(
)
. *
!
! !
ln
6
5
4
R
l
l k k
2
=
−
(
)
ln
!
! !
11
10
7
R
l
l k k
3
2
=
−
(
)
*
!
! !
ln
21
20
13
R
l
l k k
4
100
=
−
(
)
*
!
! !
ln
1039
970
6328
T
able
6. T
he
I
mpact
of
D
ifferent
R
elations
(S
elected
from
T
able
5)
on
the
N
umber
of
M
atched
-L
ines
, C
omputational
T
ime
as well
as
V
alidity
and
C
apacity
-F
actors
over
the
F
irst
to
T
hird
datasets
.
Proposed
relations
First Dataset
Second Dataset
Third Dataset
No. of
Match
Lines
Comp.
Time
(m.)
No. of
Match
Lines
Comp.
Time
(m.)
No. of
Match
Lines
Comp.
Time
(m.)
R
1
75
0.35
61
0.28
25
1.99
R
2
75
0.55
61
0.17
26
3.05
R
3
75
1.20
61
0.25
26
5.13
R
4
75 50.45 61
6.64
26 25.14
T
able
7. S
elected
V
alues
of
T
hresholds
for
the
P
roposed
SLIM
The selected values for
impact-factors of HQPS-phase
The thresholds used in
screening-procedure
Stopping-
criterion
p
1
p
2
p
3
p
4
T
1
T
2
T
3
R
2 1.5 2.5 3
2°
0.1 6*
NA
R
2
T
able
8. T
he
C
omparative
R
esults
between
the
P
roposed
SLIM
and
RANSAC O
ver
the
F
irst
to
T
hird
D
atasets
1
st
Dataset
2
nd
Dataset
3
rd
Dataset
Matching
Method
No. of
Match
Lines
Validity
Factors
(%)
Capacity
Factors
(%)
Comp.
Time
(m.)
No. of
Match
Lines
Validity
Factors
(%)
Capacity
Factors
(%)
Comp.
Time
(m.)
No. of
Match
Lines
Validity
Factors
(%)
Capacity
Factors
(%)
Comp.
Time
(m.)
SLIM 75
100
100
0.77 61
100
100
0.18
26
100
83.9
3.33
RANSAC
-
-
-
-
64
64.1
67.2
8.22
17
52.9
29.0
32.13
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING
May 2016
373


