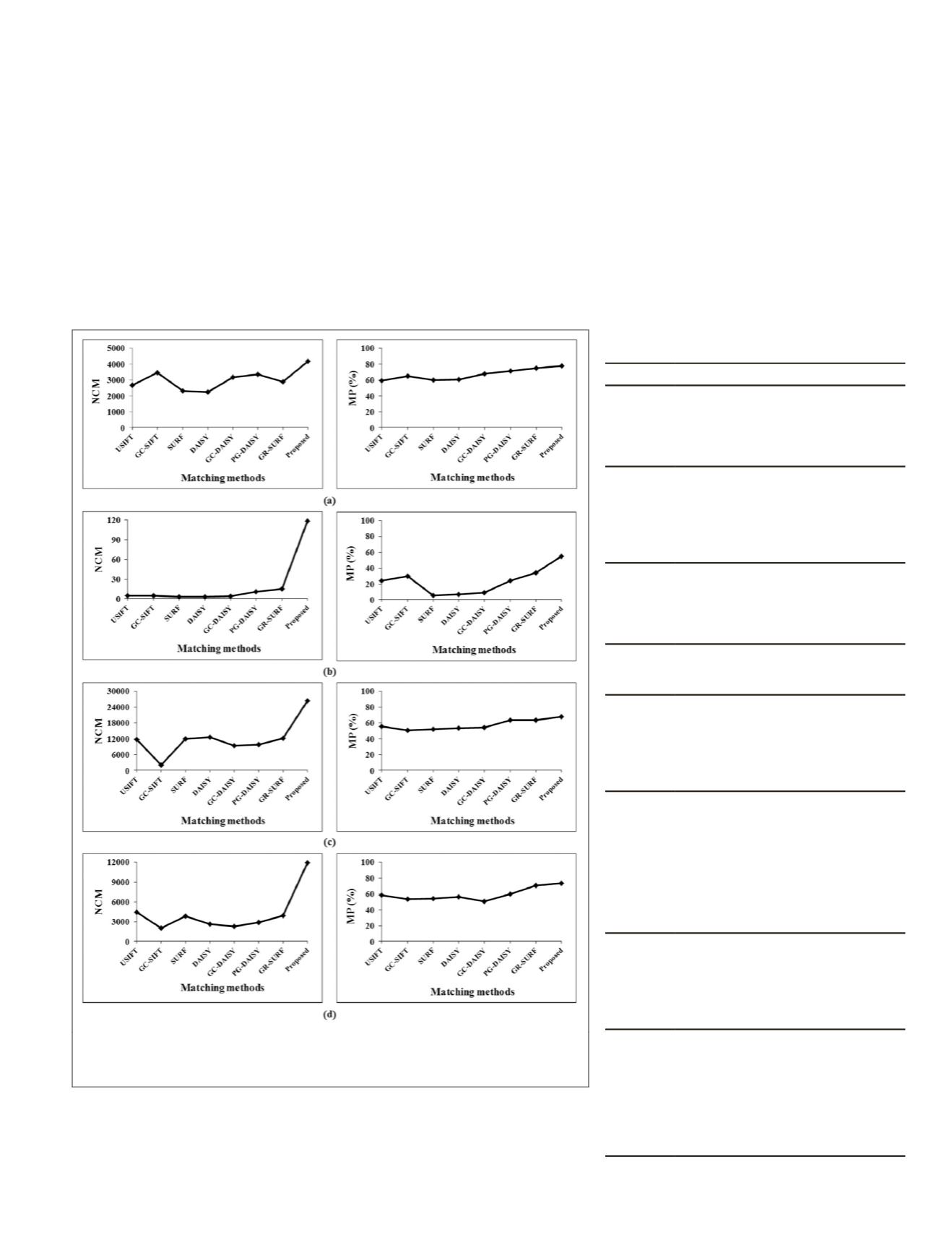
performs better than the
GC
-
DAISY
and
GC
-
SIFT
methods, as
it incorporates geometric constraints such as distance of the
points. In the
PG
-
DAISY
method, the constructed point pair
increases the feature support region and improves the feature
distinctiveness compared with isolated point, which subse-
quently improves matching performance. However, there are
many repetitive pairs due to the large number of repetitive
patterns in the experiment dataset, thus the improvement is
relatively limited.
GC
-
DAISY
and
GC
-
SIFT
methods do not pose
geometric constraints in their methods, which in consequence
lead to worse results than
PG
-
DAISY
. We observed that the
incorporating global context did not increase the distinctive-
ness of descriptor on our data, while often leaded to ambigu-
ous matches. The
GC
-
SIFT
and
GC
-
DAISY
methods obtained the
worst matching performance in most cases except dataset 1,
which is an idea pair with very similar angle and coverage.
Whereas in other datasets, there are significant translations
between images, which limits the global context information
being fully utilized and generates potentially false matches.
The
USIFT
,
SURF
and
DAISY
methods obtained worse results
than the other three (the proposed method, the
GR-SURF
and
the
PG
-
DAISY
method). It can also be seen that the proposed
method comparatively obtained much better results than the
others on Dataset 2. This is because that the brightness and
contrast, as well as the texture difference of the images in da-
taset 2 are low, leading to less distinctive feature points. Since
the proposed method seeks for local structures to distinguish
differences in repetitively textured area, it greatly improves
the matching precision (
MP
).
Table 5. All compared methods in this
experiment.
Methods
Description
USIFT
An improvement of the
SIFT
method
(Lowe, 2004) based on Harris detector,
USIFT
descriptor (uniform feature
support region size and orientation) and
NNDR
matching strategy
GC-SIFT
An improvement of the
SIFT
method
for repetitive patterns matching
by using
SIFT
descriptor to encode
local feature information and using
global context (
GC
) to encode global
information (Mortensen
et al.
, 2005).
SURF
A popular point matching method
including integral-image-based feature
points detector, Haar-wavelet-based
descriptor and
NNDR
matching
strategy (Bay
et al.
, 2008)
DAISY
A point matching method based on
DAISY
descriptor and
NNDR
matching
strategy (Tola
et al.
, 2010)
GC-DAISY
An improvement of the Daisy method
for repetitive patterns matching by
using
DAISY
descriptor to encode
local feature information and using
global context (
GC
) to encode global
information (Fan
et al.
, 2011)
PG-DAISY
An improvement of the Daisy method
for repetitive patterns matching by
matching pairs of interest points to
reduce the local ambiguities caused by
repetitive patterns and finding point
correspondences from the matched
pairs based on a compatibility
measure computed from distance
constraint (Fan
et al.
, 2011)
GR-SURF
An improvement of the SURF method
for repetitive patterns matching using
geo-referencing information of remote
sensing images to constrain the cor-
responding features searching in the
matching processing (Habib
et al.
, 2016)
Proposed
The proposed matching method
based on the proposed
LDF
detector
(for reference image), the proposed
FIPS (for searching image), the
USIFT
descriptor based on uniform feature
support region size and orientation,
and
NNDR
matching strategy based on
coarse geometric constraint
Figure 10. Matching results of different methods: (a) to (d) shows the
matching results based on Dataset 1-4, respectively. In each group of results,
the left one is the
NCM
values and the right one is the
MP
values.
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING
August 2018
521


