pairs with adjacent dates. The former image is used as input
data to predict the latter one. In the testing stage, the 2
nd
, the
3
rd
, the 6
th
, the 7
th
, the 10
th
, and the 11
th
images are selected as
input data to predict the adjacent date behind them. In this
experiment, the number of cycles is set to 300, and a total of
33 264 subimage blocks are cropped as a training set.
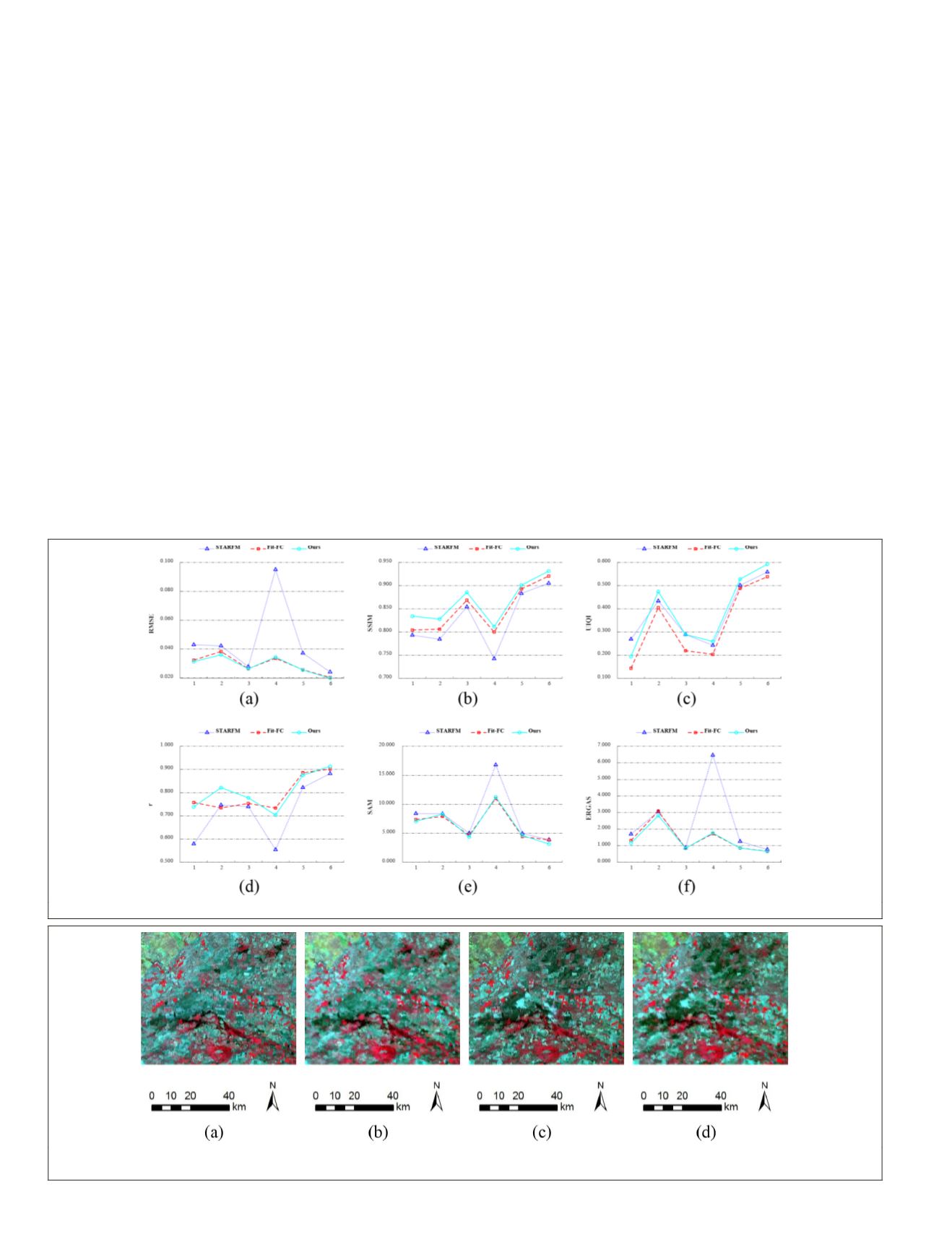
The fusion results of six image pairs in Experiment 2 are
shown in Figure 6. As can be seen from the figure, compared
with
Fit-FC
and
STARFM
, the proposed algorithm has higher
SSIM
,
UIQI
, and r values. It shows that the prediction results of
the proposed algorithm can capture more spatial information
and have stronger correlation with the real image. Compared
with
STARFM
,
Fit-FC
and the proposed algorithm have smaller
RMSE
,
ERGAS
, and
SAM
, which shows that the two algorithms
have better spectral fidelity, robustness and prediction accu-
racy for this research area.
In order to make a more detailed analysis of the fusion
results in this study area, the fusion results of 29 January 2005
are selected for further analysis. The Landsat-
MODIS
images ac-
quired on 13 January 2005 and the
MODIS
image acquired on 29
January 2005 are used as input data to predict the Landsat im-
age on 29 January 2005. These images are shown in Figure 7.
The fusion results of
STARFM
,
Fit-FC
and the proposed
algorithm are shown in Figure 8, in which the partial area
is enlarged to show more detailed information. In general,
compared with the fusion result of
STARFM
algorithm, the
prediction results of Fit -FC and the proposed algorithm are
more similar to the real image. From the perspective of the
magnified area, the fusion result of the proposed algorithm
captures more spatial details and spectral information, which
is the closest to the real image. From the quantitative evalua-
tion results of the three algorithms in Table 2, it can be seen
that although two bands of band 5 and band 7 have smaller
RMSE
values in our fusion result, the other bands are not sig-
nificantly different from the optimal
RMSE
values. The fusion
result of
Fit-FC
algorithm has the smallest
SAM
and largest r,
which indicates that
Fit-FC
has better spectral fidelity in this
study area than the other two methods. However, the predic-
tion results of the proposed algorithm have the smallest
ERGAS
and the largest
UIQI
, which shows that the fusion results of
the proposed algorithm are more similar to the real image,
and the quality is higher than the other two algorithms. In
addition, although the
SSIM
values of four bands for the fused
result of
Fit-FC
are slightly higher than our method, for the oth-
er two bands, the
SSIM
value is greatly improved. Moreover, in
combination with the
SSIM
values of the fusion results of the
six images performed above, the proposed algorithm still has
a good ability to capture the spatial structure of the image.
Conclusions
In this paper, a two-stage spatiotemporal fusion method is
proposed. Considering the large spatial resolution gap and the
complex correspondence between Landsat image and
MODIS
image, the input images are firstly preprocessed to the transi-
tional resolution between
MODIS
image and Landsat image, a
Figure 6. Quantitative assessment results for Experiment 2. (a)
RMSE
, (b)
SSIM
, (c)
UIQI
, (d) r, (e)
SAM
, (f)
ERGAS
.
Figure 7. Observed (a) Landsat image in 13 Jan 2005, (b)
MODIS
image in 13 Jan 2005 and predicted, (c) Landsat image in 29
Jan 2005, (d)
MODIS
image in 29 Jan 2005.
912
December 2019
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING


