used:
MLR
,
MLPNN
,
SVR
, and
MVRVR
. The results obtained were
then compared to examine their ability to retrieve the
AGB
from multitemporal
ALOS
PALSAR
imagery. In this respect,
80 percent of all the field data sets were chosen for training,
and the remaining were used to validate the models through
a five-fold cross-validation approach, in which the original
sample was randomly partitioned into five equal size sub-
samples. Then, a single subsample was selected as validation
data for testing the model, and the remaining subsamples
were used as training data. The cross-validation process was
then repeated once for each of the five subsamples to obtain
the validation data (Geisser, 1993).
In the
MLR
model, the backscatter values were entered into
a regression function to calculate the
RMSE
and R
2
values.
MLPNN
is a type of machine learning model that acts as a func-
tion approximation technique for estimating the nonlinear
behavior of the relationship between two separate data spaces.
To begin with, let us propose that
x
is a vector of the source
space (multitemporal
ALOS
PALSAR
backscatter values) and
that
AGB
is a scalar quantity in the target space (forest biomass
values). In this respect, the relationship between source and
target spaces can reasonably be written as:
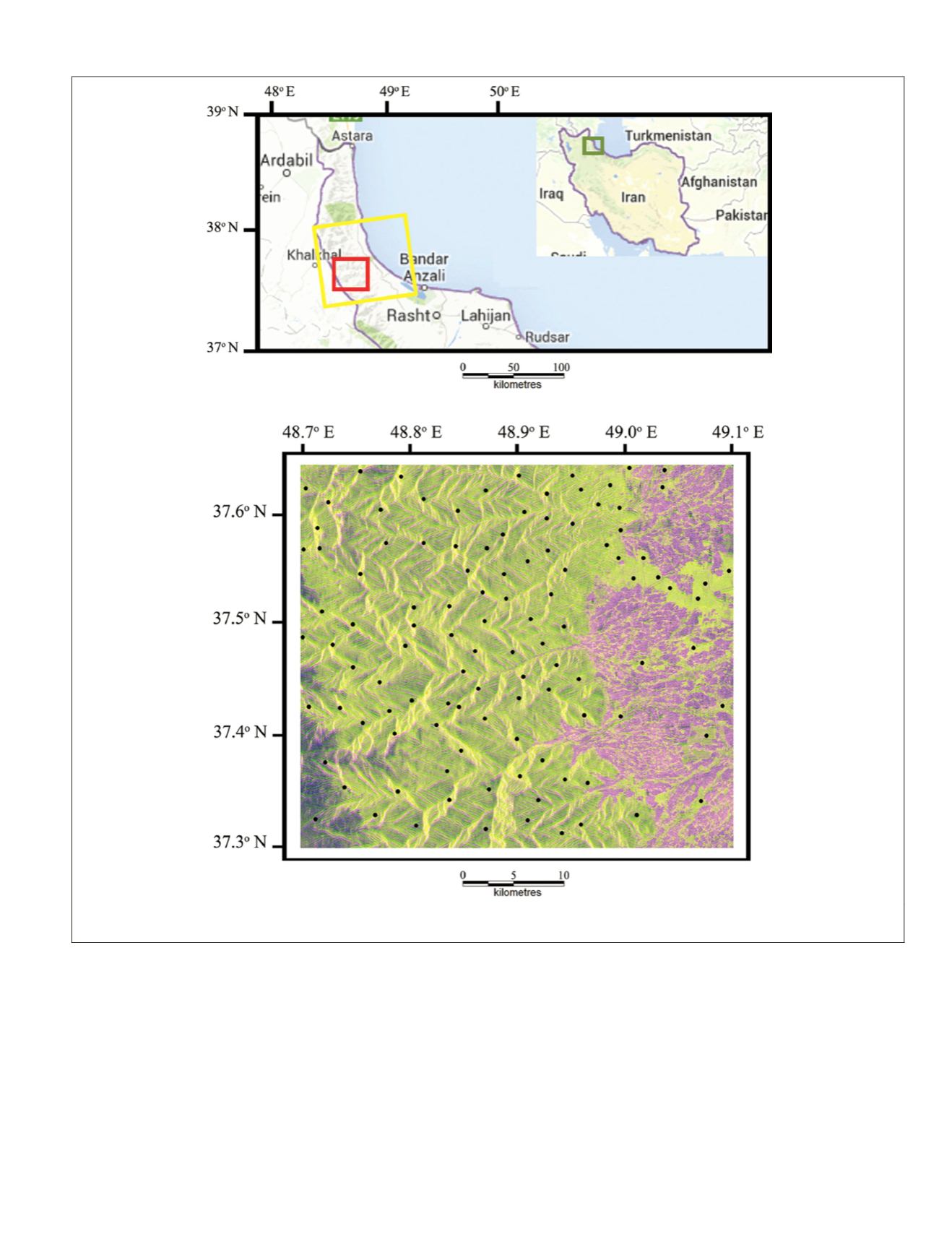
Plate 1. (Upper panel) Position of study area (red), and (Lower panel)ALOS PALSAR FBD scene (yellow); (lower panel) a topographically normal-
ized PALSAR image of the study area taken on 25 July 2010 (R: HH, G: HV, B: HH-HV; Light Green: Forest) with location of plots (black circles).
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING
January 2016
43


