T
able
1. S
ummary
of
the
P
erformance
of
the
ZY-3 C
ameras
and
O
rbit
Specification
Value
Camera
GSD
Nadir: 2.1 m
Forward and backward: 3.6 m
Multispectral: 5.8 m
Incline angle
(without
side-swing)
Nadir : 0°
Forward: +22°
Backward: −22°
Orbit altitude
505 km
Base-height ratio
0.89
Speed
~7.9 km/s
Swath Width
Single-view
52 km
Stereo
47 km
Orbit
measurement
accuracy
On-board
5 m (tri-axial, 1
σ
)
Post-processed
≤
0.1 m (tri-axial, 1
σ
)
Attitude
measurement
accuracy
On-board
≤
2.5" (tri-axial, 1
σ
)
Post-processed
≤
1.2" (tri-axial, 1
σ
)
Tri-axial
stability
Pitch direction: 3×10−4 °/s (3
σ
)
Rolling direction: 1.5×10−4 °/s (3
σ
)
Yawing direction: 1.5×10−4 °/s (3
σ
)
Time synchronization accuracy
≤
20 µs
T
able
2. G
eometric
A
ccuracy
E
stimation
for
the
ZY-3 S
atellite
W
ithout
GCP
s
Type of attitude and
orbit measurements
Planar
accuracy
Vertical
accuracy
On-board
11.3 m
12.7 m
Post-processed
4.6 m
6.1 m
Note: The planar accuracy represents the estimated planar accuracy
for the nadir panchromatic image and the vertical accuracy repre-
sents the estimated vertical accuracy of the forward intersection of
forward and backward stereo images.
As seen in Table 2, in the absence of
GCP
s, the
ZY-3
im-
ages produced by on-board attitude and orbit measurements
displayed a planar accuracy of ~11 m, which is higher than
the Chinese planar accuracy requirements of 1:50 000 topo-
graphic maps (i.e., 25 m). However, the vertical accuracy of
~13 meters was lower than the vertical accuracy requirements
for 1:50 000 topographic maps (i.e., 6 m). Thus, the images
produced by on-board attitude and orbit measurements are
only applicable to planar 1:50 000 topographic mapping. The
ZY-3
images produced by postprocessed attitude and orbit
measurements showed planar and vertical accuracies of 5 and
6 m, meeting the Chinese geometric accuracy requirements
for 1:50 000 topographic maps and being applicable to stereo
mapping of the same scale.
Experimental Verification
In this study, the experimental verification has been divided
into two parts including the planar accuracy verification and
the vertical accuracy verification, with
SC
imagery used as
experimental data.
Planar Accuracy
Study Data
An experimental area of ~3,500,000 km
2
in mid-western
China, involving high mountains, hills, and plain terrains,
with a variable elevation from altitude, i.e., 100 to 8,000 m,
was used. Nine hundred points collected in February 2012
to June 2014, measured by static
GPS
, with planar and verti-
cal accuracies higher than 0.5 m, were used as check points
(
CKP
s) and 556 panchromatic nadir
SC
images acquired in 01
June to 31 October 2013 were used as experimental images
(Figure 3). The images were produced using on-board orbit
and attitude measurements.
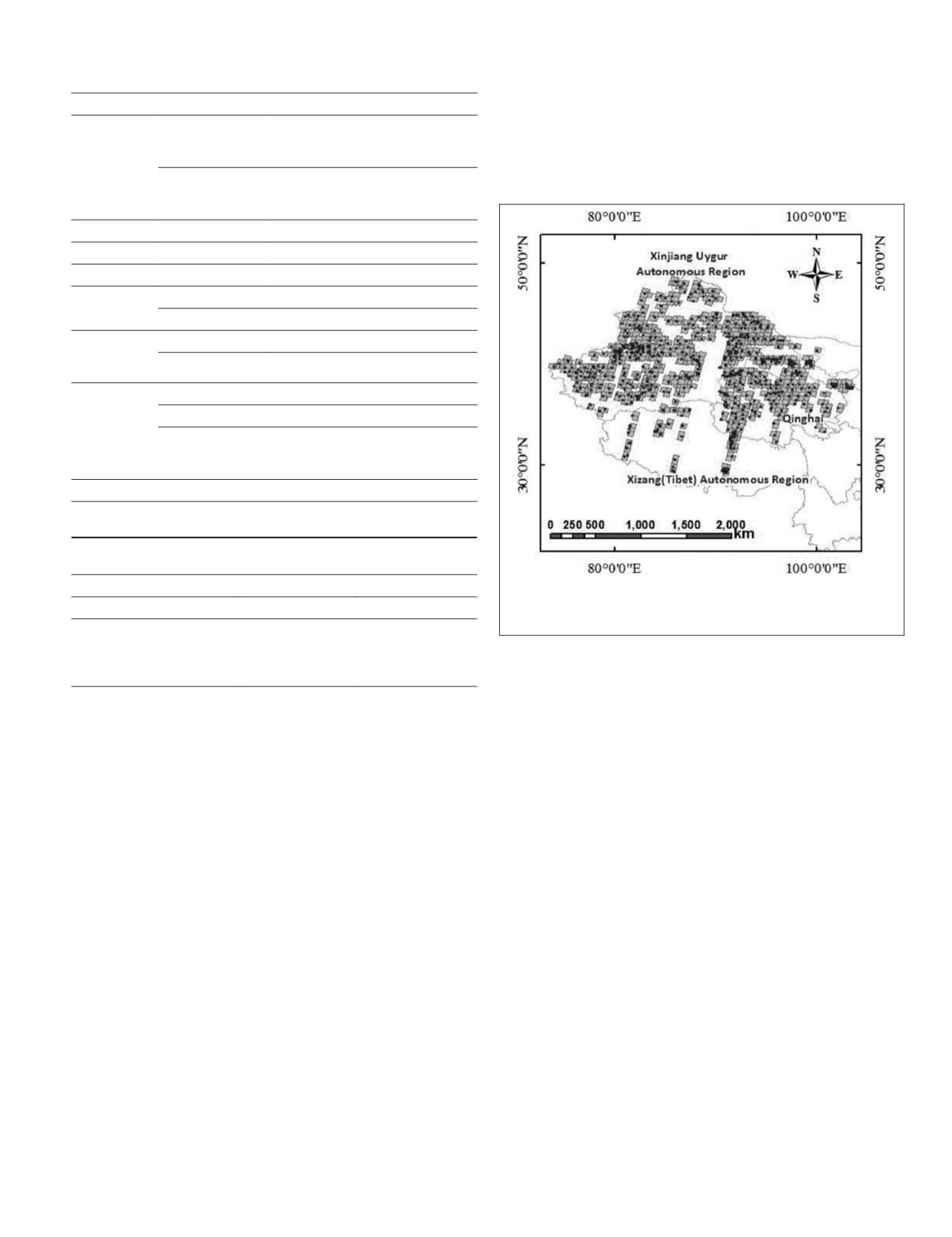
Figure 3. Distribution of the experimental images and CKPs for
planar accuracy verification. Regions represent ZY-3 images, and
points represent check points.
Experiment and Results
The transform algorithm that converts the ground-based 3D
Cartesian coordinates to the image coordinates was construct-
ed using the rational function model (
RFM
) of experimental
images (Dial
et al.,
2004; Fraser
et al.,
2005). Then, the image
coordinates of the
CKP
s for the
SC
images were calculated us-
ing the ground-based 3D coordinates of the
CKP
s. Additional-
ly, the image coordinate of the
CKP
s in the experimental image
was simultaneously acquired by manually picked, with an
accuracy of the point measurement of 0.5 pixels. The image
coordinates of checkpoints acquired by the aforementioned
two methods was compared, to obtain the planar accuracy of
the
SC
nadir images.
The experimental results proved that the planar
RMSE
of
all the
CKP
s was 5.18 pixels. Then, a calculated 2.1 m ground
sample distance (
GSD
) of the nadir image, corresponded to
~10.9 m. The maximum error was 22.5 pixels, corresponding
to ~47.2 m. More than 97 percent of the
CKP
s achieved planar
accuracy value of less than 25 m. Histograms of the residual
error of all
CKP
s were produced to illustrate the statistical
properties of the data (Figure 4).
Our results revealed that when using on-board attitude and
orbit measurements, the planar accuracy of the nadir image
reached 10.9 m, fully meeting the planar accuracy require-
ments for Chinese 1:50 000 topographic maps. The actual
experimental results agreed with the estimated planar accu-
racy of the images produced using on-board attitude and orbit
measurements (i.e., 11.3 m, calculated by Equation 20) and
the correctness and reliability of the planar accuracy estima-
tion model was confirmed.
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING
December 2015
931


