Proposed Orientated Least Square Matching
In this section the proposed orientated least square match-
ing method namely,
OLSM
is described. The input of the
OLSM
method is a set of initial conjugate elliptical features extracted
using
MSER
and Harris-affine algorithms. An example of initial
matched pairs selected by the proposed method is illustrated
in the Figure 3. These initial conjugate points are introduced
to the proposed
OLSM
method, and their positional correspon-
dences significantly improve to obtain high accurate matched
points.
The key idea of the proposed
OLSM
method is orienting
both the shape and the size of the matching window in the
search image to deal with the significant geometric distortion
between two wide baseline images.
The initial corresponding elliptical region pairs detected
with the
MSER
and Harris-Affine approach generally cover the
same part of the deformed image captured from adifferent
viewpoint, which provide rich information of geometric dif-
ferences of each other. The location, shape, and direction of
the matching window are estimated in the search image using
obtained information from conjugate ellipse pair comparison.
Local affine invariant feature algorithm simultaneously
detects the location and ellipse shape of local structures. An
affine-invariant feature comprises three components: location
l
, a 2 × 2 covariance matrix
s
defining the ellipse shape, and
dominant orientation
θ
.
The proposed
OLSM
matching method uses a window size
of
w
×
w
pixels around the feature point in the reference im-
age as a template. Then, the orientations and ellipse shape
information of each feature pair are used to approximate the
matching window shape and direction in the search image.
Let
f
r
(
l,s,
θ
) and
f
r
(
l
′
,s
′
,
θ
′
) denote a putative matched pair be-
tween reference image and search image respectively (Figure
4a). As previously mentioned, the dominant orientation is
assigned to each extracted feature based on local image gradi-
ent directions after feature affine normalization (Figure 4b).
The proposed
OLSM
accurate affine-invariant image matching
algorithm can be summarized as follows.
First, the dominant orientation difference (
Δ
θ
=
θ
–
θ
′
) of
two matched points is computed. Then, two scale factor
λ
x
and
λ
y
in the
x
and
y
directions, are estimated based on the
comparison of the semi axes of two matched ellipses. For this
purpose, the project of the semi axes of two matched ellipses
in the
x
and
y
directions (
p
a
,
p
b
,
p
′
a
,
p
′
b
) are compared after
considering the impact of the dominant orientation difference
Δ
θ
for the second ellipse (Figure 4c). After computing the
project of the semi axes, two scale factor
λ
x
and
λ
y
in the
x
and
y
directions are computed as:
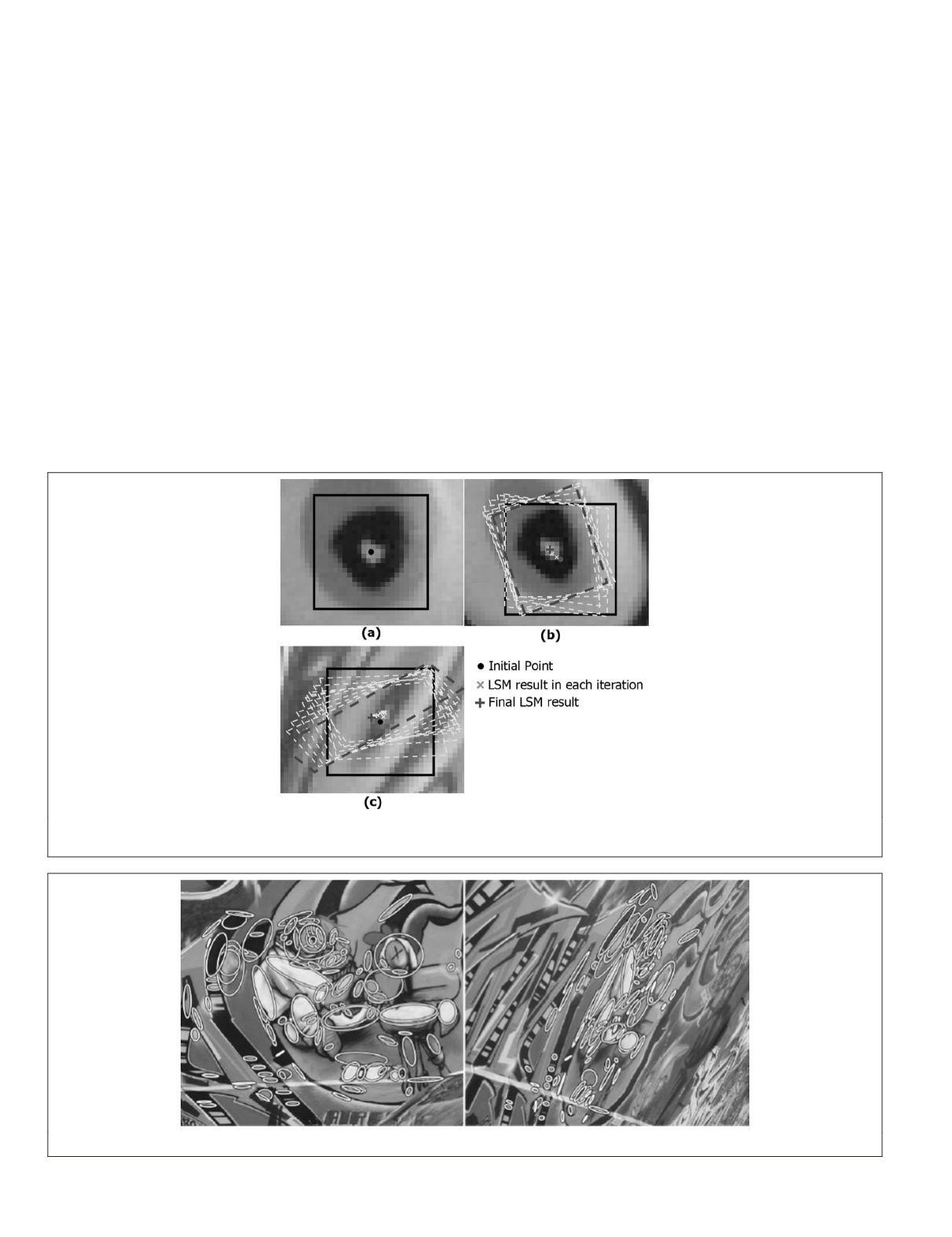
Figure 2. Example of
lsm
matching result: (a) template in the reference image, (b) successful
lsm
in an search image with non-significant
geometric distortion, and (c) unsuccessful
lsm
in an search image with significant geometric distortion.
Figure 3. Initial corresponding features detected with
mser
algorithm for first and sixth images of the graffiti dataset.
736
September 2015
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING


