as Hessian-Affine,
IBR
, and
EBR
. It should be noted that the pro-
posed
OLSM
method only uses the simple least square match-
ing methods. Clearly, various existing extensions of the least
square, such as weighting matching window (Shin and Muller,
2012) may also be applied in the proposed
OLSM
approach. For
future work, the authors are going to evaluate the proposed
OLSM
matching method in images captured from 3
D
scenes
with significant local distortions and also multi-sensor remote
sensing images. To determine the reliable window size for the
proposed
OLSM
method, the various window sizes should be
tested, which can be considered as another future study.
References
Aanæs, H., A.L. Dahl, and K. Steenstrup Pedersen, 2011. Interesting
interest points,
International Journal of Computer Vision
,
97(1):18–35.
Barandiaran, I., M. Graña, and M. Nieto, 2013. An empirical
evaluation of interest point detectors,
Cybernetics and Systems
,
44(2-3):98–117.
Bay, H., A. Ess, T. Tuytelaars, and L. Van Gool, 2008. Speeded-
up robust features (SURF),
Computer Vision and Image
Understanding
, 110(3):346–359.
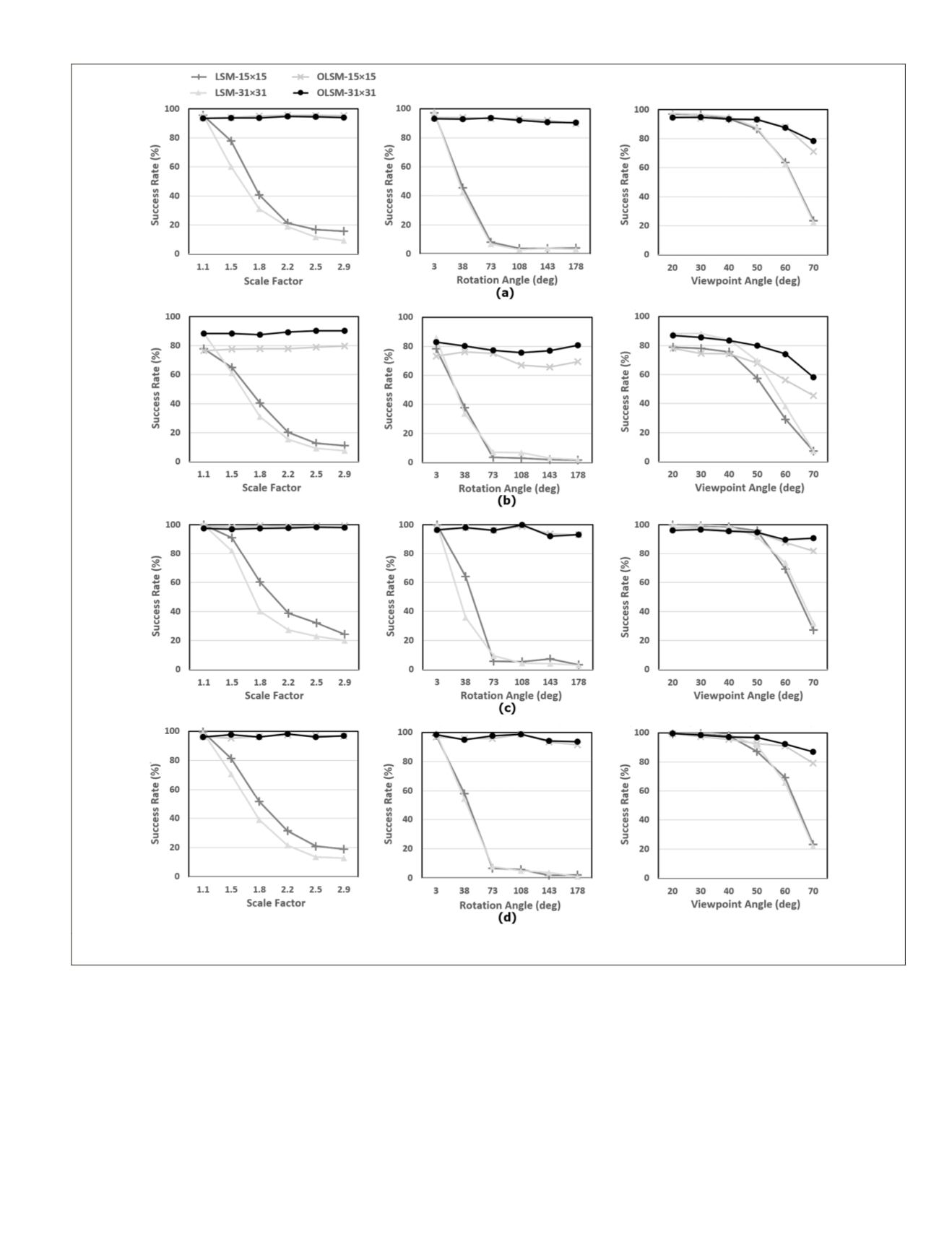
Figure 9. Success rate results on the inter-band simulated image pairs for scale (left), rotation (middle), and viewpoint (right) geometric
distortion: (a) first image:
ubc
, (b) second image: Graffiti, (c) third image:
spot5
, and (d) forth image: Worldview
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING
September 2015
741


