Rather, the incorporation of the additional spatial information
extracted by the fractal logic inversely disturb the consistency
of spectral information recorded in the original images for
these classes. Besides, for the land cover type such as water,
it may be the least ideal to consider texture analysis based on
moving windows if it mostly involves rivers, which is the case
in this study. The reason is rivers tend to have a linear shape
and are often unable to occupy enough spatial extent covered
by a given moving window. So, even if their local texture is
uncovered by these windows, these features are more than
likely to include others not really relating to water. Given this
condition, the conjunction of spatial information would disar-
range water’s regular distribution across space, leading to one
of the poorest classification results in the current study. The
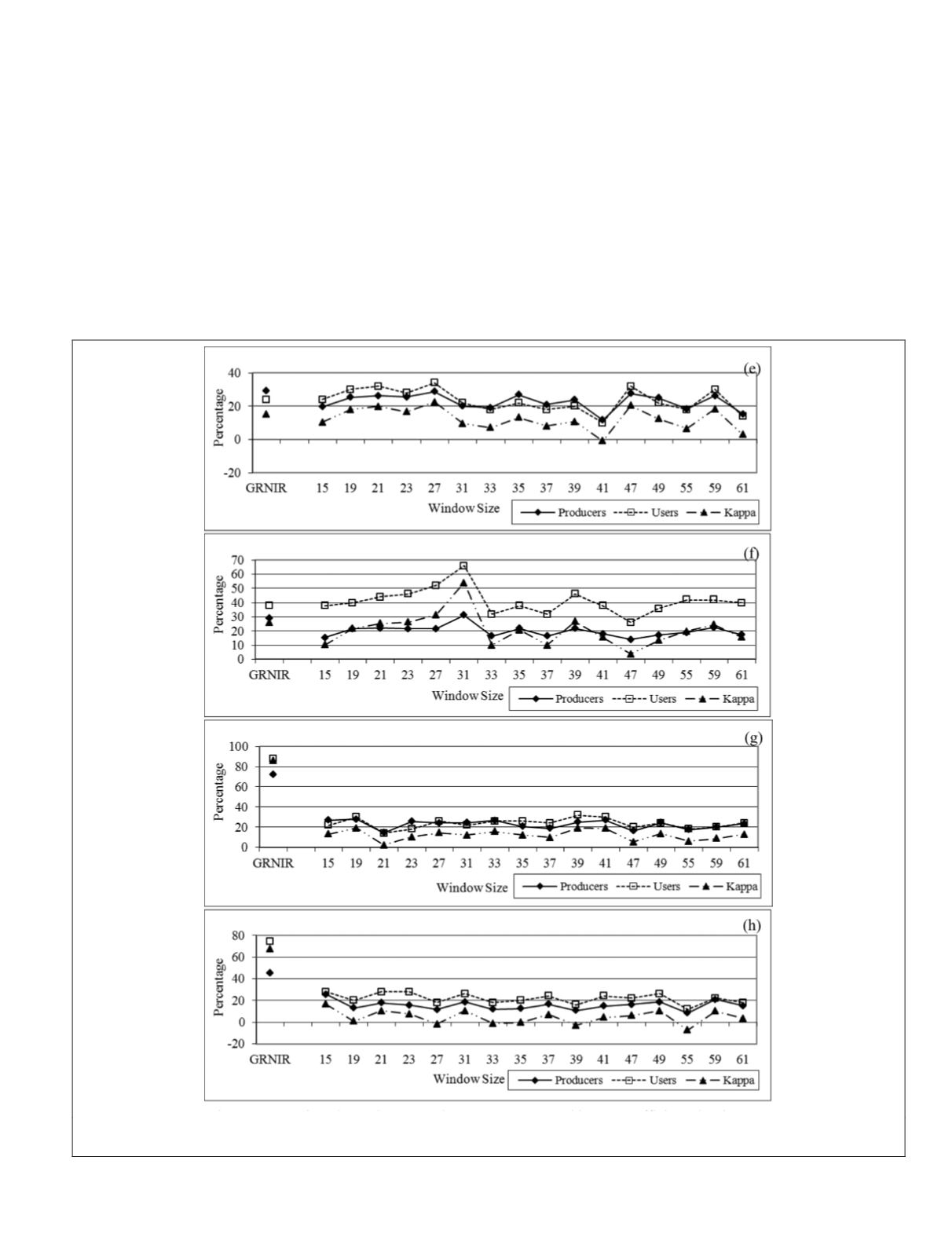
texture feature seems to only improve cropland and pasture
and medium residential slightly (about 7%) at the 31 and 27
windows, respectively. Nevertheless, the major contribution of
adding the fractal-based texture information to the
ML
classifi-
cation is the improvement of mapping low density residential
as its Khat is increased about 26% at the 31 window. With a
complicated mixture of all kinds of inputs (rooftops, lawns,
tree crown, paved street, and driveway), the residential class is
potentially hard to be spectrally separated and classified and a
finer subdivision within this group (high-, medium, and low-
density) is obviously even more challenging to achieve. When
the fractal texture algorithm is applied, the distinct spatial
patterns of medium- and low-density residential are quickly
captured and utilized for image classification. For the high
density residential identification, however, neither spectral
nor textural classification is effective. The visual comparison
Figure 9. (Continued) Producer’s and user’s accuracy and kappa coefficients by the spectral classification (
GRNIR
) and the
textural classification for medium density residential (e), low density residential (f), forest (g), and grass (h).
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING
November 2018
705


