ο ε ε
i
i
01
1 01
= +
(24)
The occlusion angle
ο
i
02
conditional on no occlusion in
the left image require that the projection of tree 0 in the right
image be conditioned by it being visible in the left image.
Moreover, in order to estimate the integral in Equation 20,
ο
i
01
and
ο
i
02
, and henceforth
ε
01
and
ε
02
, should be expressed as a
function of
d
01
. Thus, let
α
01
and
α
02
be the azimuthal angles
formed by the visual line from the left and right cameras to
tree 0 with the camera baseline (Figure 5a) and
α
i
1
and
α
i
2
the
analogous angles for tree
i
.
ε
01
depends on the diameter and
distance to the device of tree 0, which in turn depends on
the horizontal distance and the terrain slope in the direction
towards tree 0 (Equation 25),
σ
max
being the maximum slope in
the plot and
α
σ
max
the direction upslope.
x
m
(
)
(
)
(
)
ε
σ
α α
σ
01
0
01
01
2
2
= ⋅
−
(
)
asin
DBH
cos atan tan cos
ma
ax
d
/
(25)
Analogously, the covering angle of tree 0 in the right image is:
x
m
(
)
(
)
(
)
ε
σ
α α
σ
02
0
02
02
2
2
= ⋅
−
(
)
asin
DBH
cos atan tan cos
ma
ax
d
/
(26)
If
δ
0
is the angular displacement between the projection of
tree 0 in the left and right images (Figure 5a) then:
α
02
=
α
01
+
δ
0
(27)
The displacement between tree 0 projected in the left and
right images can be expressed by Equation 21 (Rodríguez-García
et al.
2014 and Figure 5a). For convenience, we refer
d
02
to
d
01
:
( )
δ
α
0
01
02
=
asin baseline
sin
d
d
d
d
02
2
01
2
01
2
=
+ − ⋅
⋅
baseline
baseline
In order to calculate
ο
i
02
, we should define
α
i
01min
,
α
i
01max
as
the enclosing angles of
ο
i
01
. As Figure 5b shows,
α
i
01min
and
α
i
01max
can be expressed as:
α
α
α
α
ο
ο
i
i
i
i
i
i
01
1
01
01
1
01
2
2
min
max
= −
= +
(29)
Analogously,
α
i
02min
,
α
i
02max
are the enclosing angles of the
nonconditioned occlusion angle in the right image and can be
expressed as:
(
)
ε
ε
(
)
α
α
ε
α
α
ε
i
i
i
i
i
i
02
2
2
02
2
2
02
2
02
2
min
max
= −
+
= +
+
(30)
To calculate the occlusion angle in the right image condi-
tional on being visible in the left image, we must subtract the
azimuth angles in the right image corresponding to occluded
angles in the left image. Depending on the distance from the
tree to the device, the projection angle in the right image is
displaced along the epipolar line. Thus, the projection of tree
0 in the right image conditional on no occlusion in the left im-
age should be in the range between
α
i
01max
+
δ
0max
and
α
i
01min
+
δ
0min
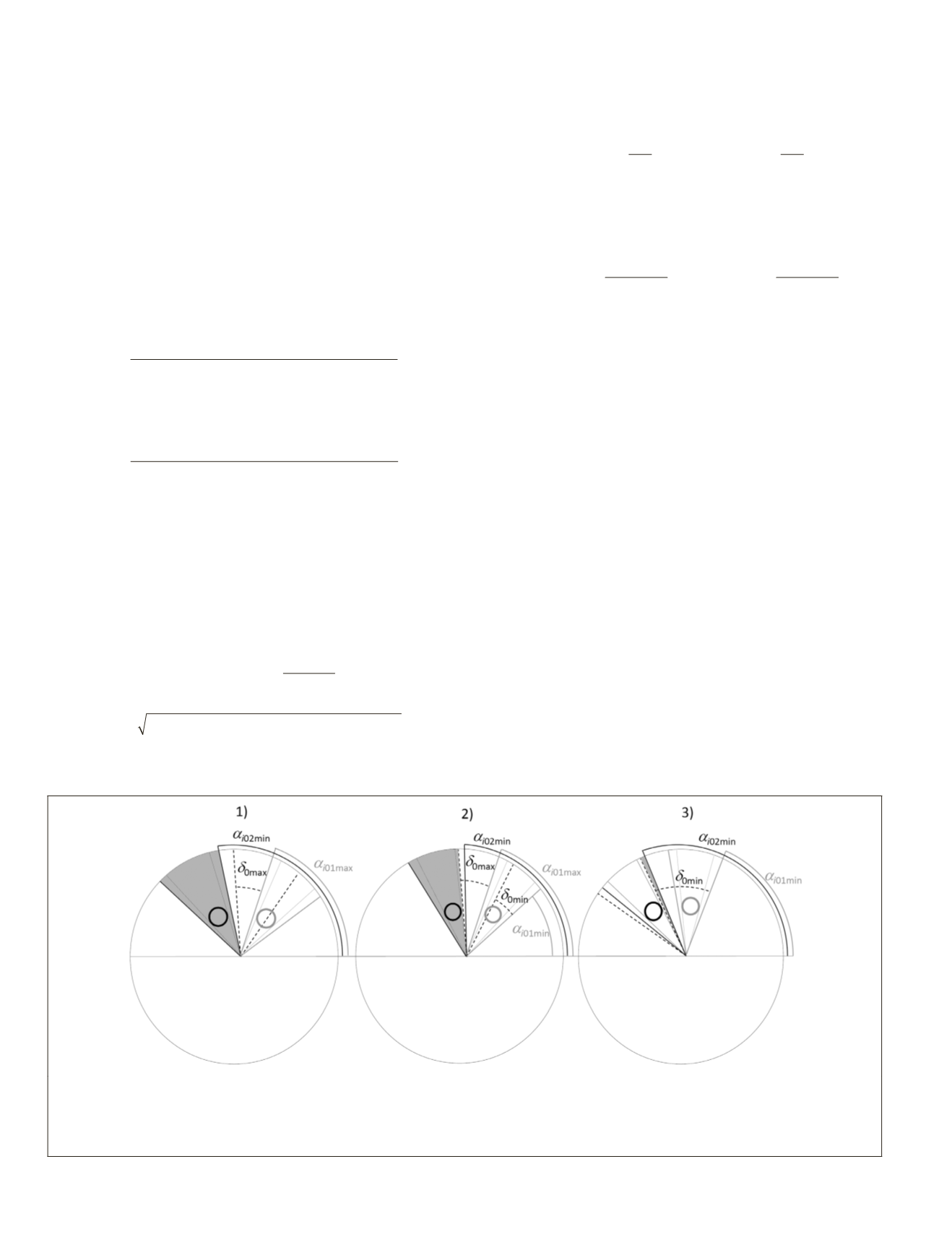
. Three cases can be distinguished (Figure 6) to calculate
ο
i
02
, depending on the angular displacement of trees
i
and 0:
Case 1.
α
i
02min
>
α
i
01max
+
δ
0max
In this case the angle shaded by tree
i
in the right image lies
completely within the range of tree 0 projection in the right
image conditional on no occlusion in the left image. There-
fore, in the right image, the occlusion angle conditional on no
occlusion in the left image coincides with the shaded angle:
=
−
ο α
α
i
i
i
02
02
02
max
min
(31)
ax
+
δ
0max
and
α
i
02min
>
α
i
01min
+
δ
0min
le shaded by tree
i
in the right image lies
range of tree 0 projection in the right
image conditional on no occlusion in the left image, and the
angular displacement of tree
i
(from left to right image) is
greater than the angular displacement of tree 0. The occlusion
Figure 6. Geometric relationships between tree 0 projected on the right image conditional on being visible in the left image,
and the shaded angle by tree
i
in the right image in the case 1), case 2), and case 3); grey lines correspond to the occlusion
angle in the left image; continuous black lines correspond to the occlusion angle in the right image; discontinuous black lines
correspond to maximum and minimum displacement of tree 0 projection from right to left image when tree 0 is occluded by
tree
i
in the left image. The grey area corresponds to the conditional occluded angle in the right image (
ο
i
02
).
500
July 2019
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING


