GPS
measurements were taken for the
GCPs
and
CPs
, using
real-time kinematics with
GPS
. Measurements were taken us-
ing a Sokkia
GRX1 GPS
. The inbuilt accuracy of the
GRX1 GNSS
receiver is 10 mm + 1 ppm (horizontal distance) and 15 mm
+ 1 ppm (vertical distance). Each point was measured four
times. The relative measurements implied that the root-mean-
square error (
RMSE
) was 12–21 mm (horizontal accuracy) and
5–7 mm (vertical accuracy). However, the expected absolute
accuracy of an RTK survey is around 2 cm horizontally and
3–5 cm vertically (Sokkia, 2012).
Result and Discussion
Camera Calibration and 3D Reconstruction of
UAV
Images
Sensor orientation and calibration are achieved by bundle
adjustment, using a geometrical perspective model. In this
study, camera calibration was performed to solve interior
orientation parameters, using
GCPs
and Pix4D software (Pix4D
Support, 2016 ). Table 4 presents the self-calibration results of
the two different cameras used in this study.
Shutter type was rolling shutter (S7) and electronically con-
trolled vertical-run focal-plane shutter (
NX
). Therefore, opting
not to use the rolling-shutter setting result in a distorted image.
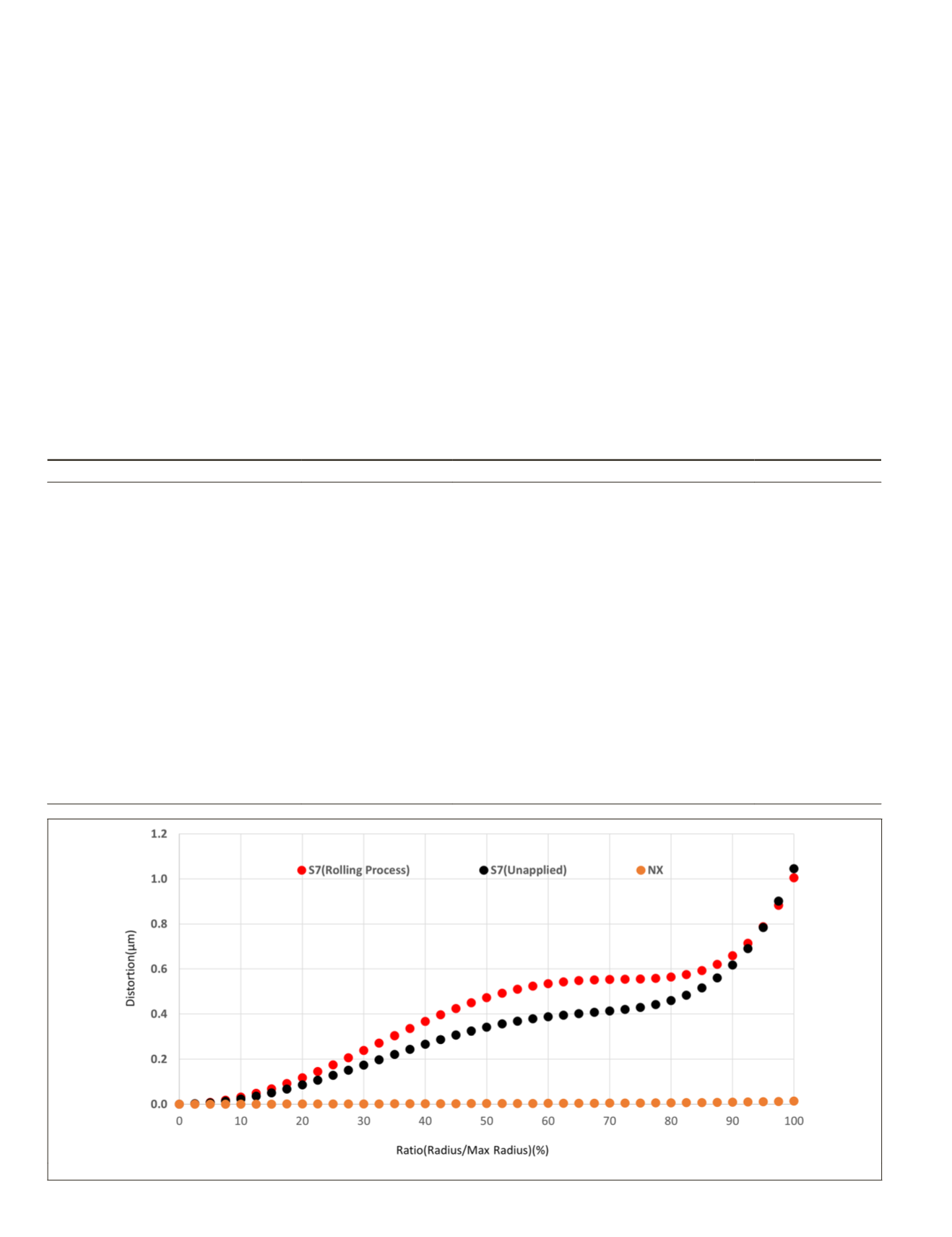
The lens-distortion ratios, based on the comparison
between the various cameras, are presented in Figure 4. The
greatest distortion ratio was observed for the S7. The S7 is
equipped with a shape-correction function. The
NX
camera
has a distortion-correction function and a highly effective in-
built lens-distortion correction option.
The bundle adjustments for the different data sets yielded
satisfactory subpixel accuracies. The matching points are the
median number of key points per image, which exceeded the
minimum number of key points per image (10,000) suggested
by Pix4D for point-cloud processing in all of the cameras.
Once the
3D
coordinates of a point were calculated, the point
was reprojected to all of the images in which it appeared. The
distance between the marked and reprojected points on an
image constitutes the reprojection error. This error is affected
by the quality of camera calibration (position and orientation)
and the quality of the marked point on the images (position
and zoom level). The mean projected error was higher for the
rolling-shutter cameras (smartphones).
Table 4. Interior orientation parameters estimated during self-calibration.
Smartphone
Smartphone (With Rolling Shutter)
Smart Camera
Camera type
S7
S7
NX
Distortion
Raw
Raw
Raw
Focal length optimum (mm)
4.102
4.317
16.151
Focal length uncertainty (mm)
0.005
0.006
0.029
Sensor format width (mm)
5.654
5.654
23.333
Sensor format height (mm)
4.240
4.240
15.556
Maximum radius (mm)
3.534
3.534
14.022
Opt. ppx (mm)
2.746
2.750
11.404
Opt. ppy (mm)
2.175
2.347
8.035
Diff. ppx (pixels)
57.778
54.406
61.525
Diff. ppy (pixels)
−39.179
−161.800
−60.269
Pixel size x, y (μm)
1.4023
1.4023
4.2641
K1
1.8642 × 10
−4
2.5293 × 10
−4
−3.2654 × 10
−5
K2
10
−5
5.4020 × 10
−8
K3
0
−6
−5.2080 × 10
−1
P1
0
−7
−2.1663 × 10
−7
P2
6.1794 × 10
−5
4.6391 × 10
−5
−1.6716 × 10
−6
Figure 4. Lens-distortion rates for the S7 and
NX
devices.
892
December 2019
PHOTOGRAMMETRIC ENGINEERING & REMOTE SENSING


